Decoding PMP Exam: Types of Questions You’ll Encounter in 2024
Over the years, the types of questions appearing in the PMP (Project Management Professional) certification exam have changed and so has the the composition, format, and number of questions.
The PMP exam has a total of 180 questions that have to be completed in 230 minutes. It is an objective type test, where in you have to select the best possible answer among the given choices.
There are mainly seven kind of questions in PMP credential exam. Among the different kind of questions, situational questions are the most numerous and also the most difficult.
Other variety of questions including direct, ITTO-based, formula based (mathematical), and professional responsibility questions have reduced over the last few years. These question types are generally easier than the situational questions.
As per PMP Examination content Outline (ECO), about 50% exam questions are from agile and hybrid project management approaches, whereas the remaining 50% questions are from predictive approaches. All questions are randomly distributed in the exam.
Let us look at different type of questions in PMP exam and understand their structure with the help of some examples.
Types of Questions in the PMP Certification Exam
1. Situational Questions
The bulk of PMP examination is made up of situational questions. In these questions, you are given a problem statement based on a scenario (small case study). These questions assess your ability to apply project management theory to real-life and practical problems.
Generally, these are very long questions and are extremely difficult to answer. You have to combine the concepts and best practices written in the PMBOK Guide (A Guide to Project Management Body of Knowledge) to answer these questions. Sometimes, all the possible answer options look to be correct. You have to pick the best choice among the given options.
As a PMP aspirant, during the PMP exam preparation, you should devote substantial chunk of your study time practicing these questions.
Example
Doug Johnson is the manager of operations at a small liquor distribution company. He has contracted an outside firm to develop a new warehouse picking system. He is generally satisfied with their performance so far, but in some meetings, he feels they are going beyond the scope of the project as it was originally defined. Doug wants to be sure only the work that is defined in the project scope is what gets done. What project documentation should Doug ask the project manager for?
- Approved scope statement, work breakdown structure (WBS), WBS dictionary, and approved changes.
- Meeting minutes from the kickoff meeting, where the project scope was discussed.
- The project charter, which defines the high level scope of the project.
- Scope baseline and schedule baseline.
Correct answer is option a. Scope Baseline is the approved version of scope statement, work breakdown structure (WBS), WBS dictionary. Scope of a project is defined in Scope Baseline and approved changes.
2. Inputs, Tool & Techniques and Outputs (ITTO) Questions
There are 49 processes across 5 Process Groups and 10 Knowledge Areas in the PMBOK Guide. Each process has numerous ITTO. In these questions, you are asked to point out the correct Input or Tool & Technique, or Output for a given process. The question can come from any process in any Knowledge Area.
About fifteen years ago, there used to be many ITTO question. Nowadays, you will seldom see ITTO questions in the PMP exam. Even thought such questions are very rare, you should practice these questions during your PMP exam prep because they help you understanding the PMBOK Guide’s concepts, which ultimately helps in answering situational questions.
Example
Which of the following is not Output to the Acquire Resources?
- Assumption log
- Resource calendars
- Change requests
- Project schedule updates
Correct answer is option a. Refer to PMBOK Guide 6th edition (Page no. 328, Figure no. 9.8.)
3. Direct Questions
Direct questions are similar to the ITTO questions. They test your knowledge about the terms and definitions written in the PMBOK Guide. These are very basic questions and can be easily solved if you have studies the PMBOK Guide properly. Just like the ITTO questions, very few direct questions appear in the exam.
Example
Product Lifecycle can be defined as:
- Collection of all the project phases
- Initiating, Planning, Executing, Monitoring & Controlling, Closing.
- Conceptualization of a new and unique product and delivering it in a specified timeline.
- Collection of all projects and operations starting from feasibility study till the retirement of the product.
Correct answer is option d. Refer to PMBOK Guide 6th edition (Page no. 19, last para.)
4. Formula Based (Mathematical) Questions
These questions are based on the formulas described in the PMBOK Guide. These questions include questions on Critical Path, Lead & Lag, Earned Value Management (EVM), and PERT Estimate.
If you have a good grasp of formulas, these questions are not very difficult to answer. Most of the formulas are small and are easy to comprehend. They do not require heavy calculations.
Like ITTO questions, the number of mathematical questions too have reduced over the last few years.
Example
Head of your engineering team tells you that a critical task will most likely take 18 months for completion. However, it might take on 15 months if everything goes well. On the other hand, it will take 45 months in the worst case. What is the expected duration of the task using the PERT formula?
- 18 months
- 12 months
- 22 months
- 60 months
Correct answer is option c – 22 months.
Calculation:
PERT Estimate = (O+P+4*M)/6
E = (15+45+4*18)/6 = 132/6 = 22 months
5. Interpretation Questions
Interpretation questions come with a set of data. You are asked to analyze the given data and deduce a logical conclusion.
These questions are new type of questions, which didn’t appear in the exam in the earlier days but these are not as tough as the situational questions. You can easily solve these questions if you have a good understanding of the pictures, tables, and graphs given in the PMBOK Guide.
Sample Question
There are two projects, Investment in project A is $6,000,000 and its NPV is $200,000. Investment in project B is $7,500,000, its net cash inflows are $5,000,000, and net cash outflows are $4,800,000. Which project should be selected if net present value (NPV) criterion is used for selection?
- Project A
- Project B
- The information in the question is inadequate
- Anyone of project A or project B
Correct answer is option d.
Explanation:
NPV of project A = $200,000
NPV of project B = $5,000,000 – $4,800,000 = $200,000.
A project with higher NPV are more beneficial than a project having lower NPV. Since both projects have the same NPV, so anyone of them can be selected.
6. Diagram Questions
These questions are often based on data tables or diagrams as described in the PMBOK Guide. You will be given a diagram or a data table and asked to answer the question based on it.
Typically, these questions are easy but just like ITTO questions, not many of these come in the present exam.
Sample Exam Question
Refer to the following network diagram and answer the question that follows. Number in the boxes represent duration of an activity. Unit of duration is days.
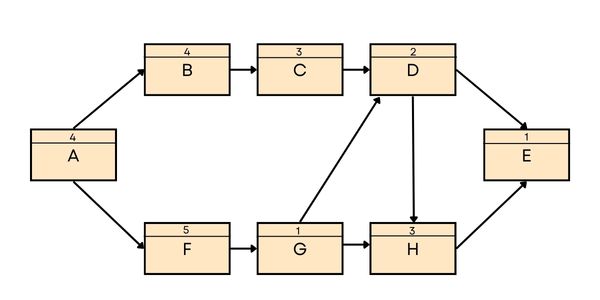
What is the total float of the critical path if management wants to do this project within 10 days?
- -7 days
- 2 days
- The total float is always 0 on the critical path
- Cannot be determined
Correct answer is option a.
Calculations:
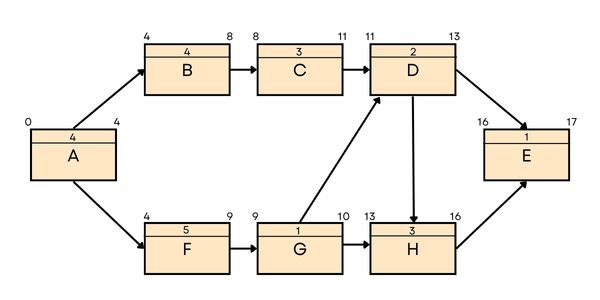
Duration of path ABCDE = 4 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 1 = 14 days
Duration of path ABCDHE = 4 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 3 + 1 = 17 days
Duration of path AFGHE = 4 + 5 + 1 + 3 + 1 = 14 days
Duration of path AFGDE = 4 + 5 + 1 + 2 + 1 = 13 days
Duration of path AFGDHE = 4 + 5 + 1 + 2 + 3 + 1 = 16 days
The longest path (critical path) is 17 days. Since the management wants to complete the project in 10 days,
Total Float = 10 – 17 = -7 days
7. Professional and Social Responsibility Questions
Project Management Institute (PMI) has defined a set of code of ethics and professional conduct for the project managers. All certified candidates should adhere to tenets defined by the PMI.
PMI poses questions based om code ethics to test if PMP candidate has understood the basic guidelines. Usually these questions too appear as situational questions and are somewhat difficult to answer.
Sample PMP Question
Which of the following are NOT part of the PMI professional code of conduct?
- Ensuring the personal integrity of others.
- Enhancing professional capabilities.
- Responsibility for actions.
- Professional conduct.
Correct answer is option a. Refer to PMI Code of Ethics.
Format of the PMP Certification Exam
There are a total of 180 questions in the exam. Out of thee,175 questions are scored and remaining 5 are not scored. These 5 questions are called pre-test questions. These questions are randomly placed on the exam, so you won’t know which questions will be scored and which are pre-test. You can read my post of number of questions in the PMP exam to understand the format of the exam.
About 50 percent of the 180 questions are based upon Agile and hybrid approaches of project management. Remaining 50% test your understanding of predictive approaches.
The test questions come in one of the following formats:
- Multiple choices: One of the four options is a correct answer.
- Multiple answers: More than one possible answer among the options.
- Matching: Match the terms/phrases in two columns.
- Hotspot: Mark the correct point/section of a diagram.
- Fill in the blanks with limited information: Only one answer is correct.
You can look at some examples of these questions in the PMI document.
Conclusion
PMP is a tough exam. You cannot pass it by memorizing the terms, definitions, and formulas written in the PMBOK Guide. You need to understand the project management concepts thoroughly while doing PMP exam preparation.
In order to successfully crack the exam, you have have thorough knowledge of the project management concepts as described in the PMBOK Guide, Process Groups Practice Guide, and Agile Practice Guide. In addition you must be familiar with all the tasks described in the PMP Exam Content Outline (ECO).
To validate your understanding of the project management cincepts, you need to do a lot of practice tests in order to become familiar with every type of question that is tested in the PMP exam.
You can refer to my article on best PMP practice exam to choose a good practice test source for your studies.
In your opinion, which type of questions are most difficult? What strategy are you following to understand these questions?
Please leave a comment below.


![Whizlabs PMI-ACP Review With Pros And Cons [2024]](https://www.pm4growth.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/Whizlabs-PMI-ACP-Review.jpg)
![Brain Sensei PMP Review 2024 [Trainings and Simulator]](https://www.pm4growth.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/Brain-Sensei-PMP-Review.jpg)

![How Many Questions Are There In The PMP Exam? [2024]](https://www.pm4growth.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/How-many-questions-in-PMP-exam.jpg)


